Mapping SFIA 8 skills to NICE work roles
The purpose of the mapping is to provide an additional dimension to the comprehensive list of NICE Work roles. This will also help SFIA users adopt NICE work roles.
The US Government's NICE Cybersecurity Workforce Framework provides a common definition of cybersecurity, a comprehensive list of cybersecurity tasks, and the knowledge, skills, and abilities required to perform those tasks.
- you can explore the detail behind these work roles on the NICE website
- NICE use a more granular approach to skills than SFIA's definitions
- NICE also list cybersecurity-related tasks, knowledge and abilities.
SFIA & NICE - cybersecurity jobs and job architectures
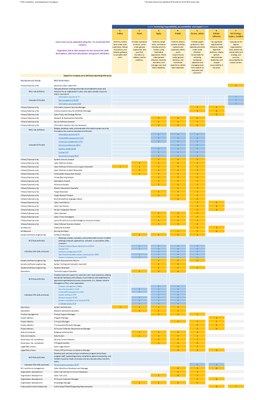
- We have developed an approach to support employers defining cybersecurity jobs and a cybersecurity job architecture based on the NICE work roles and SFIA
- We have used the SFIA responsibility levels and SFIA skills to create a simple tabular mapping to NICE work roles
- This is a work in progress, prototype of this approach
- We are looking for feedback from the SFIA and cybersecurity community to develop this further including to extending to a wider range of professional career families
- Visualising NICE roles and career steps
-
The illustration below shows how SFIA - a common language for skills - can be used to support a range of national and international cybersecurity role frameworks.
-
identify skills and adding levels of roles within the role frameworks
-
- Anyone interested in helping to develop this further should contact the SFIA Foundation
Registered users can download the spreadsheet here.
Background
- The NICE Program Office submitted a report in August 2022 "Measuring Cybersecurity Workforce Capabilities: Defining a Proficiency Scale for the NICE Framework" to Congress
- They intend to "Establish a workplace-focused NICE Framework proficiency scale that is modeled after the SFIA Levels of Responsibility and incorporates criteria of supervision, complexity, professional skills, knowledge, and influence, to be applied to Competency Areas and Work Roles; and develop a plan to communicate the scale and its application to the NICE Framework to the community of stakeholders"
- We first published a SFIA-NICE Mapping with the release of SFIA 7 (2019) and this has been updated with the release of SFIA 8 (2021) and now with the release of the NICE Framework Components v 1.0.0
These are the slides.
SFIA Skills Profiles
SFIA skills profiles for 52 information and cyber security roles published by the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) are here