End to end operating model for security
Security is everyone's responsibility. SFIA provides comprehensive coverage of the skills and competency needed to make this happen.
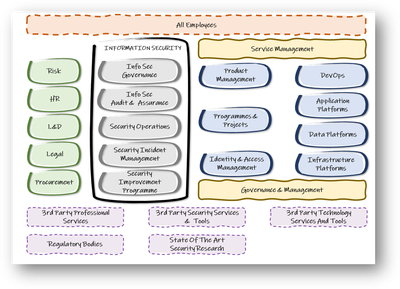
An operating model where Security is everyone’s responsibility
SFIA 8 review
One action was to be communicate how the current, SFIA 7, framework supports an operating model and a culture where security is everyone's responsibility
Here we a look at a worked example to show how security-related responsibilities are to be found across the organisation.
We then map those responsibilities to SFIA skills and SFIA generic levels of responsibility.
We are exploring the interaction between "security specialists" and the other roles where security is part of the day-to-day activities.
This work is informed by framework mappings and the analysis of all SFIA skills.
- This model is not an organisation structure - its not describing reporting structures or team names or sizes.
- It is used to illustrate the breadth of business and technology capabilities - where security must be built-in, by design and default not an afterthought
- We can use this to map security-related responsibilities to each of these components
- To execute those responsibilities, we need people with skills, knowledge and levels of competency
- SFIA provides a single solution to describe specialist skills alongside the other skills needed to build in security
Individuals and organisations embed secure working practices into everything they do.
- Security is embedded in the organisation’s culture.
- Leaders role model required behaviours.
- Security is a generally accepted part of every-day working and management practices.
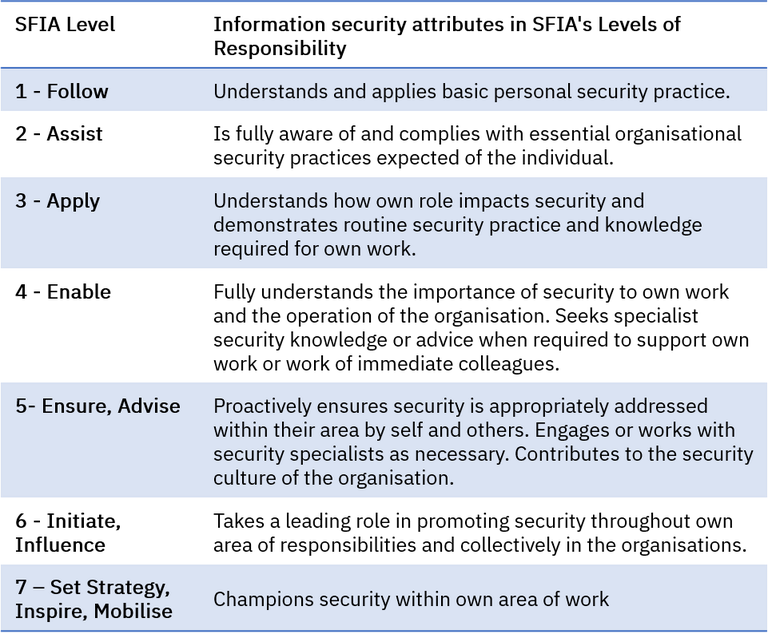
In SFIA - these expectations described in the Business skills dimension of SFIA's 7 levels of responsibility.
Table of SFIA components to security responsibilities
|
Security operating model component |
Specific security related responsibilities |
Addressed in SFIA by |
Relationship between security specialist |
|---|---|---|---|
All employees |
Employees receive regular cyber security awareness training, and know how to recognise and respond to security threats. Security is embedded in the organisation’s culture. Senior leaders role model required behaviours. Security is a generally accepted part of every-day working and management practices. |
SFIA generic levels of responsibility reference security for all levels 1 through 7 Organisation design and implementation ORDI Performance management PEMT Learning and development management ETMG Competency assessment LEDA Learning design and development TMCR Learning delivery ETDL Professional development PDSV Broad suite of professional skills supporting a comprehensive security operating model |
Info Sec organisation provides advice, guidance and support .
Info Sec specialists may be involved hands on in design and/or delivery of some education and awareness activity. |
Infrastructure, hosting, network platform |
Maintain inventory of the platform’s assets - Ensure infrastructure assets are secure during operations Define and implement controls necessary to protect platform assets in accordance with security requirements Document and enforce secure development lifecycle QA / Testing for security requirements Definition and management of identities and the access controls based on identities Understand the cause and effect of security vulnerabilities, Configuration management, patching, systems hardening Implement remedial actions to resolve vulnerabilities and recover from incidents – integrate with platform work queues Validated backup and recovery capability for critical data Monitor for potential security violations
|
IT Management ITMG IT infrastructure ITOP Network design NTDS Network planning NTPL Network support NTAS Programming/software development PROG Testing TEST Systems integration and build SINT Configuration management CFMG Security administration SCAD Penetration testing PENT Problem management PBMG Storage management STMG Asset management ASMG Knowledge management KNOW Availability management AVMT Systems software SYSP
|
Platform is responsible for day-to-day security activities and monitoring and reporting against security frameworks.
Info sec specialists have oversight of their security working practices to provide security assurance.
Info Sec specialists provide advice, guidance and support to the platform team
|
Projects and programmes |
Early identification and engagement of security resources Security risk assessments and plans Security requirements included in solution and product design Threat modelling |
Project management PRMG Programme management PGMG Solution architecture ARCH Requirements definition and management REQM Business analysis BUAN Business modelling BSMO Methods and tools METL Business process testing BPTS |
Projects /programmes are responsible for day-to-day security activities and monitoring and reporting against security frameworks.
Info sec specialists have oversight of their security working practices to provide security assurance.
Info Sec specialists provide advice, guidance and support to projects /programmes . |
Product management |
Early identification and engagement of security resources Security risk assessments and plans Security requirements included in solution and product design Threat modelling Legal requirements (GDPR and Intellectual Property Rights) Integrity requirements (the ability to prevent a fraudster changing pricing information on a web site) Protection of brand including logos and web sites. |
Product management PGMG Solution architecture ARCH Requirements definition and management REQM Business analysis BUAN Methods and tools METL Information content publishing ICPM Information content authoring INCA User research URCH User experience analysis UNAN User experience design HCEV User experience evaluation USEV Customer service support Selling SALE Sales support SSUP |
Product management are responsible for day-to-day security activities and monitoring and reporting against security frameworks.
Info sec specialists have oversight of their security working practices to provide security assurance.
Info Sec specialists provide advice, guidance and support to product management teams. |
Identify and access management |
Defining and managing identities (for people, objects, and assets requiring access (information, technology, facilities) Defining and implementing access controls based on identities and access rights Including passwords, PINs, digital signatures, smart cards, biometrics |
Security administration SCAD Conformance review CORE Facilities management DCMA |
Identify and access management are responsible for day-to-day security activities and monitoring and reporting against security frameworks.
Info sec specialists have oversight of their security working practices to provide security assurance.
Info Sec specialists provide advice, guidance and support to Identify and access management. |
Application platform |
Maintain inventory of the platform’s assets Ensure platform assets are secure during operations Define and implement controls necessary to protect platform assets in accordance with security requirements Document and enforce secure development lifecycle QA / Testing for security requirements Definition and management of identities and the access controls based on identities Threat modelling - understand the cause and effect of security vulnerabilities, Configuration management, patching, systems hardening Monitor for potential security violations Implement remedial actions to resolve vulnerabilities and recover from incidents – integrate with platform work queues |
Systems development management DLMG Software design SWDN Programming/software development PROG Testing TEST Systems integration and build SINT Configuration management CFMG Application support ASUP Security administration SCAD Penetration testing PENT Problem management PBMG Asset management ASMG Knowledge management KNOW Availability management AVMT |
Platform is responsible for day-to-day security activities and monitoring and reporting against security frameworks.
Info sec specialists have oversight of their security working practices to provide security assurance.
Info Sec specialists provide advice, guidance and support to the platform team |
DevOps |
Maintain inventory of assets Define and implement controls necessary to protect assets in accordance with security requirements Document and enforce secure development lifecycle and ensure assets are secure during operations DevSecOps - Implement security decisions and actions at the same scale and speed as dev and ops decisions & actions. Integrate security into suite of tools automating devops QA / Testing for security requirements Definition and management of identities and the access controls based on identities Threat modelling - understand the cause and effect of security vulnerabilities, Monitor for potential security violations Configuration management, patching, systems hardening Implement remedial actions to resolve vulnerabilities and recover from incidents – integrate and prioritise with team work queues |
Systems development management DLMG Software design SWDN Programming/software development PROG Testing TEST Systems integration and build SINT Configuration management CFMG Application support ASUP Security administration SCAD Penetration testing PENT Problem management PBMG Asset management ASMG Knowledge management KNOW Availability management AVMT IT Management ITMG IT infrastructure ITOP Network design NTDS Network planning NTPL Network support NTAS Methods and tools METL
|
DevOps team is responsible for day-to-day security activities and monitoring and reporting against security frameworks.
Info sec specialists have oversight of their security working practices to provide security assurance.
Info Sec specialists provide advice, guidance and support to the DevOps team |
Data platform |
Maintain inventory of information assets Designate, prioritise, and categorise information and vital assets - informed by the criticality and sensitivity of the information asset Create / maintain data model with visibility to the location of sensitive information Use metadata to manage sensitive data Ensure information assets are secure during operations Define and implement controls necessary to protect information assets in accordance with security requirements Document and enforce secure development lifecycle QA / Testing for security requirements Definition and management of identities and the access controls based on identities Threat modelling Monitor for potential security violations Understand the cause and effect of security vulnerabilities, Configuration management, patching, systems hardening Implement remedial actions to resolve vulnerabilities and recover from incidents – integrate with platform work queues Validated backup and recovery capability for critical data |
Information governance IRMG Data management DATM Storage management STMG Security administration SCAD Conformance review CORE Facilities management DCMA Data modelling and design DTAN Database design DBDS Database administration DBAD Programming/software development PROG Testing TEST Systems integration and build SINT Configuration management CFMG Application support ASUP Security administration SCAD Penetration testing PENT Problem management PBMG Asset management ASMG Availability management AVMT |
Platform is responsible for day-to-day security activities and monitoring and reporting against security frameworks.
Info sec specialists have oversight of their security working practices to provide security assurance.
Info Sec specialists provide advice, guidance and support to the platform team |
IT management and governance |
Governance structures and processes Clear governance structures and defined lines of responsibility and accountability Board level commitment and involvement Measuring and monitoring of performance Continuous improvement of security capabilities and outcomes Create/maintain enterprise data model with visibility to the location of sensitive information |
Enterprise and IT governance GOVN Information security SCTY Organisation design and implementation ORDI Strategic planning ITSP Measurement MEAS Sourcing SORC Supplier management SUPP Enterprise and business architecture STPL Information governance IRMG Data management DATM IT management ITMG Systems development management DLMG Business risk management BURM Demand management DEMM Portfolio management POMG Quality management QUMG Organisational capability development OCDV |
IT management and governance are responsible for day-to-day security activities and monitoring and reporting against security frameworks.
Integrate security into governance working practices. E.g. measurement and tracking
Info sec specialists have oversight of their security working practices to provide security assurance.
Info Sec specialists provide advice, guidance and support to IT management and governance. |
Service management |
Managing security as a service Integrate security best practices into service management best practices – to lower cost of maintaining acceptable security levels, effectively manage risks and reduce overall risk level Accrediting systems to from a security perspective to operate in the live environment appreciate the significance of changing the configuration and ensure that the impact on security is considered The security of the configuration system itself Include a security review into the formal release and deployment process |
Service level management SLMO Release and deployment RELM Service acceptance SEAC Configuration management CFMG Problem management PBMG Incident management USUP Availability management AVMT Capacity management CPMG Solution architecture ARCH Methods and tools METL Business process improvement BPRE |
Service management are responsible for day-to-day security activities and monitoring and reporting against security frameworks.
Integrate security into service management working practices.
Info sec specialists have oversight of their security working practices to provide security assurance.
Info Sec specialists provide advice, guidance and support to service management. |
Risk |
Manage/address risks from poor information security in the same way all other business risk Information security risk management is the critical first area of ensuring an organisation designs, develops and implements IT systems that have security by design and default. Review security issues that might affect the organisation and reviewing them in light of the business requirements Develop a pragmatic, sensible and cost-effective solution managing the risk down to an level that is acceptable to the senior management. Independently review security measures on a regular basis, Ensure audit results are reviewed and assessed by senior management. |
Business risk management BURM Conformance review CORE Information assurance INAS Information security SCTY |
Info Sec specialists provide advice, guidance and support to service management. |
HR/Learning & development |
Recruitment and onboarding process Candidate vetting, Terms and conditions of employment, Acceptable use policies Generic or role based accountabilities in job descriptions Objective setting and performance management Effective job design and separation of duties Broad awareness education for security Developing, planning, coordinating, and evaluating training/education courses, methods, and techniques Developing and conducting training or education of the workforce Workforce plans, strategies, and guidance |
Performance management PEMT Resourcing RESC Relationship management RLMT Organisation design and implementation ORDI Learning and development management ETMG Competency assessment LEDA Learning design and development TMCR Learning delivery ETDL Professional development PDSV |
HR / Learning & development are responsible for day-to-day security activities and monitoring and reporting against security frameworks.
Integrate security into HR / Learning & development working practices.
Info sec specialists have oversight of their security working practices to provide security assurance.
Info Sec specialists provide advice, guidance and support to HR / Learning & development. |
Procurement/supplier management |
Management of 3rd party suppliers - cloud services, applications, ERP systems, RFPs, operational supplier management Supply chain risk assessment, Due diligence, contracting, Annual supplier assessment |
Sourcing SORC Supplier management SUPP Continuity planning COPL Contract management ITCM Relationship management RLMT |
Procurement/supplier management are responsible for day-to-day security activities and monitoring and reporting against security frameworks.
Integrate security into procurement/supplier management working practices.
Info sec specialists have oversight of their security working practices to provide security assurance.
Info Sec specialists provide advice, guidance and support to procurement/supplier management |
Information security governance |
Governance & Risk Management Board-level commitment and involvement Information Security - strategy, policies and processes Central inventory of relevant data regulations and the affected data subject area Security metrics, reporting and tracking Security architecture 3rd party / managed security services |
Enterprise IT governance GOVN Information security SCTY Information assurance INAS Measurement MEAS Business risk management BURM Enterprise and business architecture STPL Supplier management SUPP |
|
Information security audit & assurance |
Compliance ensure that controls are adequate to meet security requirements Conduct security audit and assessments External validation Support for internal and external audits |
Information assurance INAS Measurement MEAS Conformance review CORE Testing TEST |
|
Information security operations |
collating external and internal security intelligence, conducting situational awareness – reporting an operational view of the external environment analysing and managing threats to the organization’s information security security information and event management - real-time analysis of security alerts generated by network hardware and applications. log management – collecting and storing log messages and audit trails managing vulnerabilities, viruses, and malicious code providing a information security help desk. managing security incidents (detection, analysis, response, and recovery) communicating with internal stakeholders and external entities, as required |
Security administration SCAD Information security SCTY Specialist advice TECH Measurement MEAS Methods and tools METL Incident management USUP Relationship management RLMT Continuity management COPL Business risk management BURM Supplier management SUPP IT infrastructure ITOP Network support NTAS Penetration testing PENT Knowledge management KNOW |
|
Security incident management /
|
Planning for incident management and response, business continuity, service continuity and disaster recovery Performing and coordinating tests, exercises, and drills of response plans Problem management, root cause analysis, and reviews after security incidents Conducting forensic investigations. Working with law enforcement and other regulatory bodies during and following an incident. Communications with key internal and external stakeholders Manage PR and reputation |
Continuity planning COPL Business risk management BURM Incident management USUP Information security SCTY Information assurance INAS Relationship management RLMT Supplier management SUPP Contract management ITCM Digital forensics DGFS |
|
Information security improvement programme |
Identify, review, assess business functions that impact information security Develop, implement, and maintain an information security improvement programme, plan, and processes Define information security roles and responsibilities Allocate trained & skilled resources to implement the programme Identify, manage, and maintain the work products required to deliver the programme Identify, involve, communicate with and report to internal and external stakeholders Allocate and manage funding for information security activities Measure and monitor cost, schedule, and performance against the information security plan |
Information security SCTY Programme management PGMG Project management PRMG Portfolio, programme and project support PROF Consultancy CNSL Organisational capability development OCDV Measurement MEAS Organisation design and implementation ORDI Relationship management RLMT Change implementation planning and management CIPM Benefits management BENM Learning design and development TMCR Learning delivery ETDL Competency assessment LEDA Professional development PDSV |
|
3rd party providers of security services and tools |
collating external and internal security intelligence, utilising machine learning, AI and other innovative tools to enhance the predictive capability of the organisation Using data visualisation to show how threats are being actioned to enable timely and effective business decision making conducting situational awareness – reporting an operational view of the external environment analysing and managing threats to the organization’s information security security information and event management - real-time analysis of security alerts generated by network hardware and applications. log management – collecting and storing log messages and audit trails |
Information security SCTY Emerging technology monitoring EMRG Consultancy CNSL Specialist advice TECH Methods and tools METL Analytics INAN Data visualisation VISL Innovation INOV Penetration testing PENT Knowledge management KNOW |
Responsible for ad hoc or day-to-day security activities – contracted by the Info Sec organisation.
Provide access to deep expertise , tools and skilled resources to enable the Info Sec organisation to meet its responsibilities. |
State-of-the-art security research |
Systematic creation of new knowledge by data gathering, innovation, experimentation, evaluation and dissemination. Determination of research goals and the method by which the research will be conducted. Participation in a community of researchers; communicating formally and informally through digital media, conferences, journals, books and seminars. Themes such as Secure systems and technology, verification and assurance, operational risk and analytics, identity, behaviour and ethics, national and international security and governance, human aspects of cyber security/human-centred computing |
Research RSCH Emerging technology monitoring EMRG Methods and tools METL Analytics INAN Data visualisation VISL User research URCH |
The Info Sec organisation does not have or need the capability to perform original research into information security.
It relies on its 3rd party suppliers or using secondary research and/or being part of security community to keep up to date with industry developments. |