SFIA 9 Home
SFIA 9 is the new version of the global skills and competency framework for the digital world - published in October 2024.
First published in 2000, SFIA has evolved through successive updates, shaped by expert input from its global users to maintain its relevance and value to industry and business needs.
SFIA began as a framework for the ICT community. It has grown into a framework that defines the skills and competencies needed by business and technology professionals who design, develop, implement, manage and protect the data and technology that power the digital world.
SFIA encompasses many of the world's most in-demand occupations, including professionals working in areas such as:
- information and communications technology
- business change
- digital transformation
- data science and analytics
- software engineering
- information and cyber security
- learning and education
- applied computing and computational science
- user centred design
- digital product development, sales and marketing
- human resource and workforce management.
SFIA 9 continues this evolution.
SFIA 9 builds on the framework’s established principles. This version incorporates numerous updates requested by industry, introducing additional skills and refining many existing ones. However, the essential values and core concepts of SFIA remain unchanged, as they have been for over 20 years.
SFIA's design principles and structure are unchanged
The widespread success and global reach of the SFIA standard stems from its reflection of industry reality. The seven SFIA levels define clear and recognisable responsibilities and accountabilities—this clarity is highly valued by SFIA users.
The structure remains unchanged: seven levels of responsibility characterised by generic attributes that describe behavioural factors, along with professional skills and competencies defined at one or more of these levels.
SFIA’s flexibility allows it to be applied across a wide range of business and professional functions. As many roles today require a mix of technical and non-technical skills, SFIA’s framework is ideally suited to reflect this blend.
The SFIA 9 content
Browsing SFIA 9 web pages
For those who want to go straight to the content of SFIA 9. Here you can find...
- Levels of responsibility
- SFIA 9 skills directory - search for and browse all the skills
- Generic attributes and behavioural factors
Themes
SFIA views
- Full framework view - skills arranged by categories and sub-categories
- Digital Transformation skills view
- Agile skills view
- DevOps skills view
- Big data/Data science skills view
- Information and cyber security skills view
- Enterprise IT - for core information and technology functions
SFIA 9 documentation
A number of documents are available for download.
You need to be registered and logged in to the site to access the documents. You can register here.
Any problems accessing documents (not for password changes) please contact [email protected]
These include:
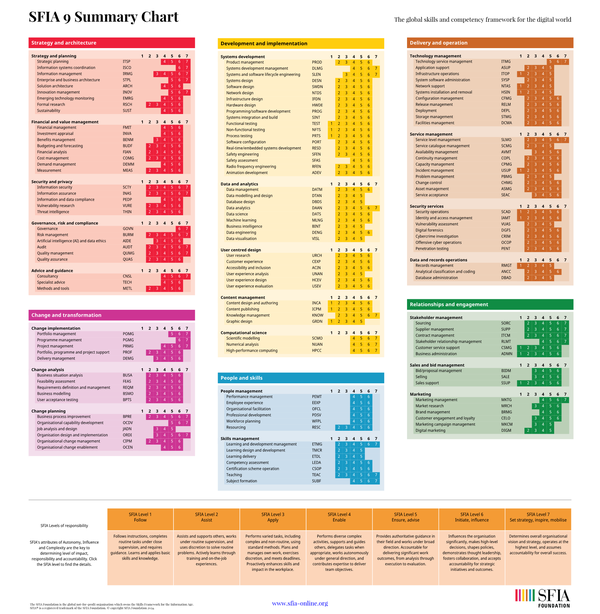
- new look summary chart - skills and responsibilities.
- to help raise awareness and common understand of the levels of responsibility
- designed for onscreen viewing with hyperlinks to SFIA 9 website content
- 2 pdf reference manuals
- skills, responsibilities, generic attributes and behavioural factors spreadsheet - for importing content for your own tools and documents
The story behind the content
How SFIA is updated
- an extensive global collaboration and consultation involving SFIA users, skills management practitioners and professional bodies
- a beta release period since July for feedback and improvement



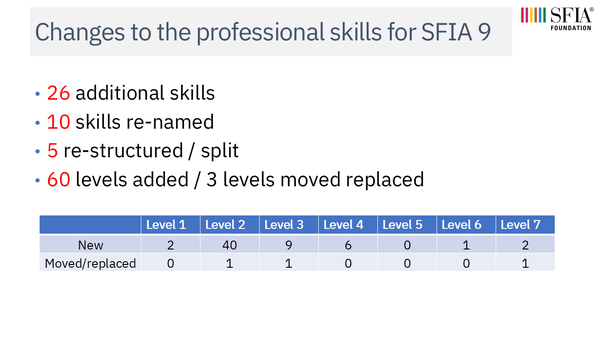
SFIA 9 content changes - the professional skills
- 26 additional skills
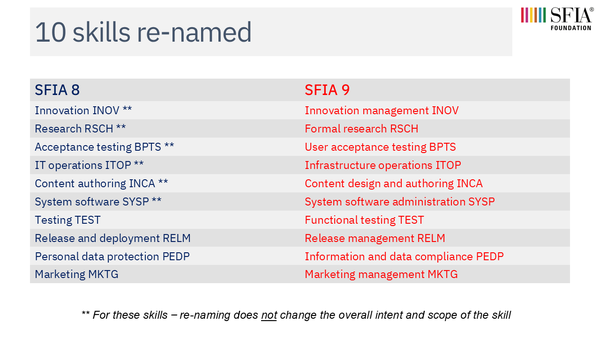
- 10 skills re-named
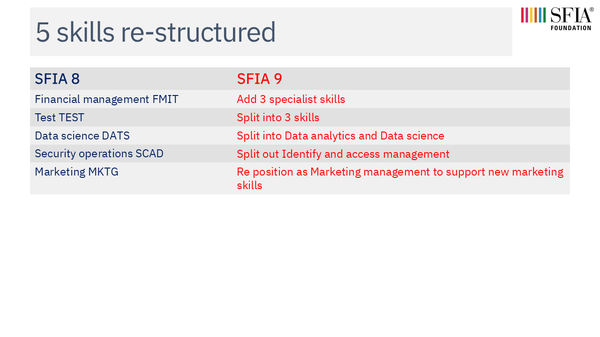
- 5 re-structured / split
- 60 levels added / 7 levels moved replaced


SFIA 9 content changes - the generic attributes
- Making SFIA’s behavioural factors easier to access and use
- Adding “Essence” statements for all levels
- Updates to generic attributes to enhance readability and consistency across levels and attributes – guidance notes added
- 2-way look up - by levels and by generic attributes
- New look graphic for the Summary chart






SFIA 9 Readability improvements
- We have continued the approach started in SFIA 8
- Significant enhancements to guidance notes to bring them to a uniform standard across all skills
- Generic attributes and behavioural factors follow the same pattern

SFIA 9 theme-related changes
As with previous updates, a number of themes were reviewed. Addressing a theme allows the framework as a whole to be reviewed for a particular context.
The SFIA 9 release notes provide comprehensive information on theme-related changes

SFIA 9 - options for navigating the SFIA framework


Moving to SFIA 9
Planning your adoption of SFIA 9
It includes
- general guidance for adopting SFIA 9 whether you are currently using SFIA 8 or previous versions of SFIA
- specific details on the content of SFIA 9 and how it has changed from SFIA 8.
- Full details here - Moving to SFIA 9

The SFIA ecosystem
More than just a skills and competencies framework
This describes some of the range of activities of the SFIA Foundation. They are not core elements of the SFIA Framework and may not be generally visible to the user community but they are key to the Foundation's activities.
Including
- User guidance
- Mappings to industry frameworks
- Links to industry bodies of knowledge
- SFIA accredited partners and specialists
- Skills mapped to standard roles
- SFIA accredited training
- Not-for-profit stewardship of the SFIA framework


Thank You to Our Community
Global Community
Our sincere thanks go to the extensive community of SFIA users - volunteers from around the world representing hundreds of organizations. Their invaluable contributions included:
- Providing requirements and suggesting solutions
- Sharing information on how SFIA is used with employers large and small
- Collaborating on framework mappings and guidance for the good of industry
- Creating and reviewing change requests
- Drafting and reviewing content
The Framework continues to be available in 11 languages. A complete list of SFIA contributors and supporters can be found here.
SFIA has become the world's most widely adopted skills and competency framework, supported by a comprehensive ecosystem that extends beyond just the Framework itself.
SFIA 9 Global Design Authority Board
Special recognition goes to the SFIA 9 Design Authority Board members who worked tirelessly, often across challenging time zones, to deliver exceptional results on behalf of the SFIA community:
Matthew Burrows
Penny Coulter
Ralph Goeckel
Peter Leather
Phil Lovell
Daniel Merriott
Grant Nicholson
Miroslav Pavlovic
Andy Thomson
Project leadership
We are grateful to Peter Leather for his dual role as SFIA 9 Update Manager and technical consultant/subject matter expert.
Ian Seward
General Manager — SFIA Foundation
Chair — SFIA Design Authority Board
October 2024
Email: [email protected]
